
Since we’re in 1-dimension, “space” means “length.” We can say that 1-dimensional packing is a linear density or line density.įor any particular direction, you need to draw a line and determine what percent of the line is covered by a circle. Remember, we want to find the space taken by atoms compared to the total space. Don’t worry! If you understand the concept, you won’t need a formula at all. Since we’re in 1D, formulas with volume don’t apply. Hexagonal Close-Packed (HCP) Structure and APFġ-Dimensional Packing Factor: Linear Density.Face-Centered Cubic (FCC) Lattice Length and APF.Body-Centered Cubic (BCC) Lattice Length and APF.Simple Cubic (SC) Lattice Length and APF.2-Dimensional Packing Factor: Planar Density.1-Dimensional Packing Factor: Linear Density.This might be a little hard to conceptualize, so let’s start by dropping into 1- and 2-dimensions. Assuming the atoms are hard spheres with radius in a cubic unit cell with lattice parameter , That means each atom has the volume of a sphere. The expanded version would look like this:Īdditionally, atomic packing factor uses the hard sphere model. In metals there is usually only one atom, but in a ceramic, suppose there are 3 kinds of atoms:, , and. Where is the volume of each type of atom. If you have multiple kinds of atoms, you need to include the number and volume of each atom.
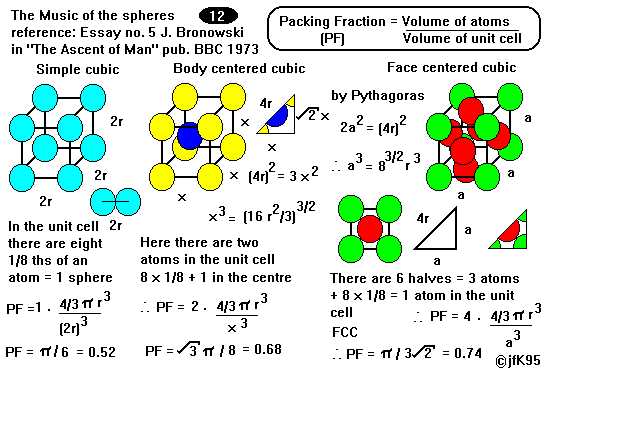
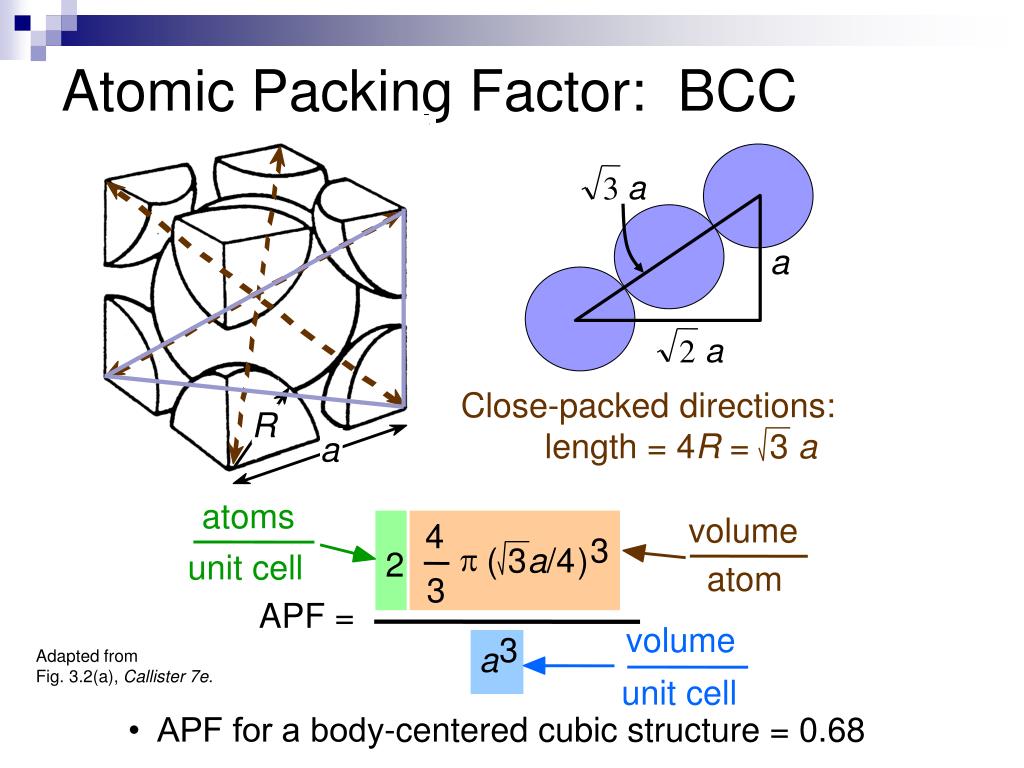
For a more complicated description of having multiple kinds of atoms, click here to expand. The unit cell is defined as the simplest repeating unit in a crystal.Īssuming all atoms have the same size, and are arranged in a repeating crystal lattice, Usually, this “repeating volume” is just the volume of the unit cell. Crystal StructureĪtomic packing factor (APF) of common crystal structures.Ĭalculating the atomic packing factor for a crystal is simple: for some repeating volume, calculate the volume of the atoms inside and divide by the total volume.
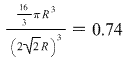
Later in the article, I explain step-by-step how to calculate them. You can think of this as a volume density, or as an indication of how tightly-packed the atoms are.įor quick reference, I have created a table below of atomic packing factor (APF) values for common crystal structures. Atomic Packing Factor (APF) tells you what percent of an object is made of atoms vs empty space.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
